Computer Science AS
Introduction Information Representation Communications Communications 2 Hardware Logic Circuits Processor Fundamentals Assembly Language Monitor & Control System Software Security, Privacy & Data Integrity Ethics DatabasesAS Practical
Algorithm Data Structures and more Software developmentComputer Science A2
Data Representation File Organisation Advance Logic GatesInternet Virtual Machines System Software Encryption & Security Artificial IntelligenceA2 Practicals
Binary Search Linear Search Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Combined Algorithm Stacks Queues Linked List Binary TreeMore
Reference Pastpaper QuestionsNetwork Hardware, ISPs, PSTNs & IP Addresses
Transmission mediums
Transmission can be either guided (wired or cable) or unguided(wireless)
For each transmission medium there are many options. So we will see for each their properties and advantages and disadvantages
Cable (guided)
Transmission which uses a wire such as twisted pair, fibre optic or coaxial cable
| Name of cable | Bandwidth | Interference | Attenuation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Twisted pair | Low | Highest | Medium |
| Coaxial Cable | Relatively high | Low | Highest |
| Fibre Optic | Highest | Lowest | Lowest |
Wireless (unguided)
Transmission which uses radio, microwave or infrared.
| Wireless | Bandwidth | Penetration | Attenuation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiowaves | Lowest | Highest | Lowest |
| Microwaves | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Infrared Waves | Highest | Lowest | Highest |
There is no clear trend for interference, however wireless transmission has more interference than wired transmission
Also the need for repeaters is less often used than for wired transmission
Depending on the situation the type of wireless transmission used depends
Understand that infrared has a short range compare to microwaves and radiowaves. For this reason we use infrared only for short range transmission
Practical uses of Wireless and Wired transmission
Wireless transmission is used in connecting mobile phones to the WAP
It is used in Lan networks to reduce the amount of cabling but usually we use twisted pair for LAN networks
Wired transmission is used for internet communications and also telephone communications
Satelites
Instead of using wired transmission for world wide communications we can use satelites which uses wireless transmission (microwaves).
There are 3 types of satelites depending on their positions
- Geostationary Satelites
- MEO - Satelites
- LEO Satelites
- Repeaters
- Bridge
- Switch
- Server
- Network interface card (NIC)
- Wireless Network interface card (WNIC)
- Wireless Access point (WAP)
- Router
- The PSTN can send both analogue signals and digital signals
- The PSTN doesn't need power for telecommuniciations but requires power for internet commmunications
- A dedicated line is made for Telecommunications
- World wide web WWW
- Cloud Computing
- Static IP address
- Dynamic IP address
These are satelites which has an orbital period of one day and it is about 35000km above the surface of the earth.
Also the satelite will positioned above the same point above the earth always.
They are usually on top of the equator
3 are required to enable global coverage and is usually used for long distance telephone communications or networks
This is called medium earth orbit satelites which is used for GPS and 10 are required for global coverage
The Low earth orbit satelites has the lowest orbital radius. Thus this is used in high speed telecommunciations and internet communications.
Usually the main reason why we don't use Satelites is because they are highly expensive and difficult to maintain and also as they are very far away they have a delay in transmission.
This delay is called latency
LAN Hardware
There are many devices or hardwares in a particular network and they have there own functions
We must know in depth the functions of each device
A device connecting two wires which provides a full strength signal to the second wire.
The reason why the word amplifier is wrong is that a amplifier boost both the interference and the signal whereas the repeater boosts the signal only.
A device which connects two segments of LAN. It records the Network addresses of the devices in each connected segment.
For example if we want to extend a bus topology with a star topology we could use a bridge and a repeater to produce a larger LAN and a hybrid network.
A central device which is used to connect devices in a star topology which can send a unicast message
So for commmunications within a particular network such as a WAN we don't need a router. All we need is a switch
The switch is the advanced version of the hub as it provides more features than the hub. The hub is also used as a central device but the message is usually send to all the other devices. This causes data collisions and thus corruptions
Is a computer which provides a specific service or an application
This is not a device but actually a component in a device which uniquely identifies a device on the internet. It contains a hard coded MAC address which is a 48 bit code in hexadecimals
This provides the NIC function in a wireless network
A central device used to connect device to a wireless network
A good example is a wireless router
However for the WAP to communicate with the device it must have WNIC
This is specially used in cell phone networks
Acts as a node on the internet
So usually the router is used when we are connecting two networks together. Actually the router we know is actually different from the ones the ISP use.The routers used by ISP actually acts a point or a node which connects other routers from other ISPs
The router also enables you to communicate with different underlying network technologies - this is actually called a gateway but is replaced by the router now.
Also as the name suggests the router finds the most suitable route for data packets to be transmitted over the internet
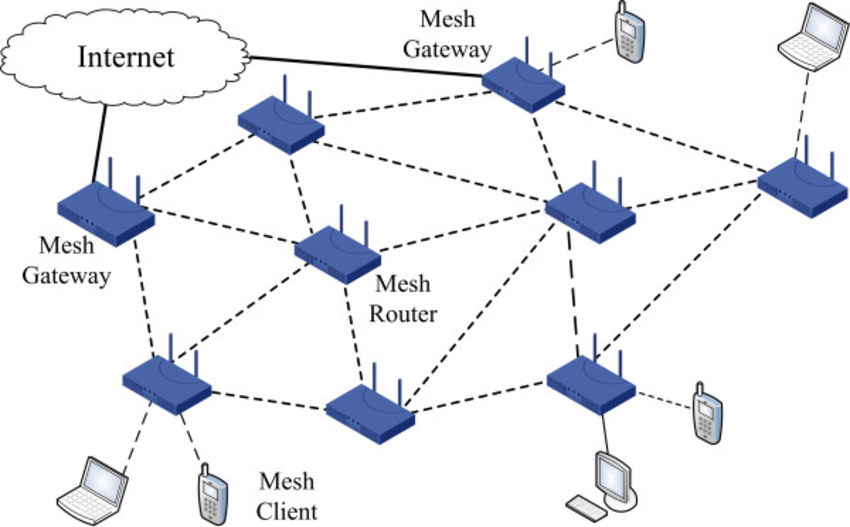
Ethernet
Is used as a wired transmission for LAN networks.
The original ethernet or also known as legacy ethernet was used in LAN networks
The central device used in early times was a hub
The hub had no control of where the data is sent and it is broadcasted to all the devices
This has a higher chance of data collisions and data corruptions
There was a method used to avoid data collisions and this is called CSMA/CD - carrier sense multiple access/ collision detection
You will need to know briefly this process
1. Firstly the transmission medium is checked if it has a voltage. If a voltage is present then it will wait a random time and try again
2. When no voltage is detected the transmission is started and there is a continous check for a collision.
3. If a collision is detected then the transmission stops and it alerts other endsystems of the presence of a collision.
4. Then it waits a random time and tries again.
.Nowadays Modern ethernet we don't use this method because a switch is used instead of a hub
The Switch can end the message to the required device. Also the switch contains a buffer which can temporarily store data until a transmission medium is freed. So then it can send data without collisions
Remember that usually the LAN network follows the star configuration.
ISP
It is a company or organisation which links a device to the internet by providing an IP address.
The fact is that this defines access ISP and there are actually many types of ISPs
So the access ISP are connected to the middle tier ISP and the middle tier ISP are connected to Tier 1 ISP.
This is indeed confusing however lets approach this logically. We know one organisation can't handle the world ISPs. So the ISP are broken down depending on their Hierachy and size.
The Tier 1 is the largest ISP and they connect Middle tier ISP to the internet. The Middle Tier ISP connects the access ISPs. The Access ISP connects users like you to the internet
Public switched telephone network (PSTN)
As we know that the PSTN is an infrastructure of the WAN network and it is owned by a company
So the PSTN owns the infrastructure which was original used for telephone communications which now is used as the infrastructure for the Internet. The transmission medium is fibre optics.
There are some important things you need to know.
It is mainly digital
So analogue signals means sound is transmitted
So telecommunications use analogue signals to transmit data
The internet transmits data in the form of digital electrical signals
As analogue signals can be transmitted without power.
Whenever you're in a call a dedicated line is made temporarily between the two telephones. However the internet uses a concept called package switching where data is transmitted in the most appropriate route, decided by the router
Application which uses the internet
You will need to know some applications which makes use of the internet
It is a distributed application which contains documents in the form of webpages structured in to websites which has been made available for anyone to access
Usually they ask what is the difference between the WWW and the internet.
So the WWW does not follow any protocols (Ex IP/TCP) and it stands for World wide web. Also it is not a network but an application which contains documents and data
Computing service provided through the internet
These services are like file servers and application servers (Ex Google Drive)
There are 3 types of Cloud computing services and it could either be public or private
Private Cloud: Cloud servers owned and maintained by organisations and are used by the organisation only.
Public Cloud: Cloud servers which are used by the public for general use
The establishment of the cloud server on a particular location must be known
The 3 types of services which are offered by public clouds:
1. Infrastructure provision - These include the hardware requirements of a computer system and so these can be used to back up files or store data or provide requirements to execute a particular software
2. Platform provision - These provide debugging services to be able to run softwares on different platforms for testing.
3. Software or application provision - similar to a application server as it contains softwares which could be used by the user
The reason why we use Public cloud servers rather than creating our own servers(private cloud) is because it is highly costly and also not alot of technical expertise are required to use public cloud services
The only problem with public cloud services are that data can be accessed by the third party. So the user must hope and trust the cloud service provider that they will maintain data security.
Bit streaming
They usually ask:
What is bit streaming?
During streaming data, data is sent in sequence of bits from the media servers to the receiver through the internet and is temporarily held in a buffer until it is played by a media software.
The above one is a brief explanation and so you need to include more points
1. There are two types of bit streaming - on demand and real time bit streaming
Real time (live feed) bit streaming is when the bits are transmitted as soon as it is captured and recorded
On demand bit streaming is when bits are streamed at a time chosen by the user
2. In bit streaming data is compressed from bytes to bits and decoded at the recieving end and so the order of bits sent is same when received
3. The buffer has a high watermark and a low watermark which maintains the amount of data stored in the buffer.
4. The bandwidth of the connection is higher than what is being played by the media softwares.
5. Requires bits to be sent at high speeds to avoid buffering
The above points are enough to score full marks
IP Addressing (Ipv4)
An Ip address is quad dotted number which uses 32 bits to store each address. Each 8 bits can be used to represent a value from 0 to 255.
Usually an ip address is in denary form
Example - 192.168.2.1
Ip addresses are provided by the access ISPs
The Ip address is used to identify a location on the internet so that data can be sent to the correct location
As Ipv4 can only represent 232 differenct address it is not enough and so there are many schemes used to use the IP addresses more efficiently.
There are two types of IP addresses
These are Ip addresses which remains permanent and doesn't change.
Changes whenever you log out and connect to the internet
Original scheme
In the original schemes the IP address were divided into fixed Class A , B or C. These Ip address use the first few bits to define the class and also contained a fixed number of bits used for Network and Host ID
The table is not required to be remembered.
The problems was that as due to the rigid number of host and network IDs. This left alot of unused number of host IDs or very little amount of Host IDs.
For example the Class C uses 21 bits to define the network ID and 8 bits to define the Host ID
So this allowed alot of networks to be provided however only 256 hosts can be connected to each network.
This caused many problems as the number of host were increasing this class was not suitable.
Classless Inter domain routing (CIDR)
In this scheme they use network IDs and host IDs however they were not arranged into fixed classes.
At the end of the IP address there was an 8 bit suffix to define the number of bits for network ID.
This made it more flexibe as the organisation can get the Ip addresses which are most suitable for them. So they can contain the right number of network connections and the number of Host connected to each network.
Also now bits are not required to define the class used so this allows more space for Host and Network IDs
Remember the above explanation are for organisations which uses a large number of networks. These include access ISP and Tier1 ISPs.
For example if the Middle Tier 1 ISP had many access ISP connected to it. It will use a IP address which have a high number of bits for Network ID and somewhat reasonable number of bits for Host .
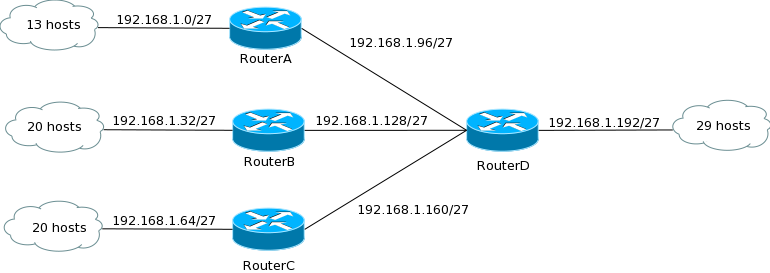
Subnetting
A large organization that contains many workstations and quite far away.
Say each of them uses a separate network and the use they 8 bits for host ID
Then each workstation can connect 256 hosts to each network but each workstation only uses 10-20 hosts, so this is gone for waste as not all the IP addresses are used in each station
To make it more efficient we use subnetting.
For this we need a router that acts as a node and stores the IP address of the hosts connected to the router.
So a single network could be used and then be divided using a router so then it can connect workstations. So rather than using separate networks, the single network can provide IP addresses for the hosts in each workstation.
In other words the network is split and each workstation gets an allocated number of IP addresses depending on the number of hosts in each workstation.
For this to occur the router must record the IP address of each host in every station.
Private Network Address- NAT
NAT is Network address translation.
We know that Ipv4 is not enough to identify each device on the internet
For this reason we use a method which requires only the (private)network address to be unique and the IP address within the Network (private address) must also remain unique. However, the private address of a particular network doesn't have to be unique among different networks
For example your router has a public address that uniquely identifies the particular network you're using. This address can not be repeated anywhere on earth.
However when you connect your device to the WIFI router you will provide an IP address called the private address which can not repeat in the same network but can repeat in a different network. So if your friend connects to the same WIFI router he will not have the same address as you. However, if he goes to his own WIFI router, he might have the same IP address as you.
So a component called the NAT box is usually installed on the router which converts the Private address to a public address before it is sent to a different server. It also keeps a log of the request sent by the individual devices on the private network.
Remember when I say the word network in this scenario it means private network - network usually in a building home or office use.
Ipv6
As Ipv4 is not enough for future use, we must use Ipv6.
It uses 128 bits to store each address, and so can represent 2128 addresses.
It is usually written in the Hexadecimal form
ffff:ffff:::ffff:ffff:ffff:1234Domain name server (DNS)
We will need to know some definition
DNS service
It is a hierarchy distributed database which is installed on the DNS servers which maps the domain name to their corresponding Ip addresses
DNS servers are the servers that contain the DNS database.
So usually as it is hard to remember Ip addresses, we use domain names to identify a particular web server or website.
The process by which the DNS servers map the domain name to the IP address is called Name resolution.
Across the world there are few DNS servers called the root servers (top-level DNS servers) and they store the domain names of the top-level domains such as .com
Sub domain servers hold subdomains in their system and the Ip address for that particular zone
Example - the Britain sub DNS servers may contain domains such as the .edu or .gov which are only related to a specific region.
Here is an example of a domain name: Revisezone.com
Name resolution
You will need to know the steps of mapping a domain name to its Ip address
1. First, the domain name is typed on the user browser, then it is sent to the DNS servers.
2. If the domain name is in the system or database then the correct Ip address is returned
3. If it is not in the database the domain name is forwarded to a different root server and follows the hierarchy of the domain name to retrieve the Ip address. This means if it was a .uk.edu it would first go to UK then the edu sub-domain servers
4. If not found the browser will check the cache memory for the old Ip address and use this instead.
Recommended
These are things you might like. Clicking these ads can help us improve our free services in the future...
End of Chapter Videos
Collection of Videos to Support Your Understanding.
Remember these videos are handpicked by me and I feel these are one of the best ones out there. But I constantly update this list for each chapter.The Youtubers are more than welcome to contact me.
Also, don't forget to Subscribe to our Youtube channel - Wiscus
Watch
