Computer Science AS
Introduction Information Representation Communications Communications 2 Hardware Logic Circuits Processor Fundamentals Assembly Language Monitor & Control System Software Security, Privacy & Data Integrity Ethics DatabasesAS Practical
Algorithm Data Structures and more Software developmentComputer Science A2
Data Representation File Organisation Advance Logic GatesInternet Virtual Machines System Software Encryption & Security Artificial IntelligenceA2 Practicals
Binary Search Linear Search Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Combined Algorithm Stacks Queues Linked List Binary TreeMore
Reference Pastpaper QuestionsDatabase, Normalisation & SQL coding
Differences between data stored in files and in Databases
There are 4 things you need to comment in the exam
- Data integrity
- Data privacy
- Data redundancy
- Data dependancy
Databases maintains the integrity of the data stored by providing validation and preventing any corrupted or incomplete data
The file just stores the data which it is being supplied with and sometimes the data could be corrupted or overwritten
Databases allow access rights which limits the users access to the data stored in the databases
Files do not have any proper access rights. However, the only method to restrict access to data is to make copies of the file and distribute the edited files to the individuals which contain the data only for that particular user
If files are distributed and copied then data is unnecessarily redundant and so this will take unneccessary storage
The database organises the data in the most efficient way possible to remove data redundancy. And also many different users of different access rights can access the same and only database
When data is stored in a file the structure of the file data must be known but, the databases uses queries to store and retrienve data without knowing how data is stored in the database(this is known as the external level).
Also when storing new data the programs may have to be changed where as in databases this is handled by the DBMS software and the users just has to add new data
Relational databases
You may have heard what databases are, it contains tables which store data
However, in AS we need to know what relational databases are
A flatline table is table which is considered to be a stand alone table and has no relation with other tables
In the relational database model the tables have links between other tables
You will need to know some new terms in this model
- Relation
- Tuple
- Attribute
- One to One
- One to many(vice versa)
- Many to many
- External level
- Conceptual level
- Internal level
- Data Definition Language (DDL)
- Data Manipulation Language (DML)
A Special type of table used in relational databases
Stores data of a particular instance or item in a relation
This is the same as a row or a record
Stores data of a particular property of an item or instance in a relation
It is same as a column or a field
Candidate key
One or more key attributes which contain unique values for each tuple
In the table(relation) there might be attributes which contain unique values. So this could be used to uniquely identify each record or tuple
Primary key
This is a candidate key which is used to uniquely identify each tuple
Each table must have a primary key as it prevents data redundancy as each tuple in the relation is automatically unique when the primary key is unique
So as we can see the primary key is chosen from the candidate keys
Secondary key
A candidate key is not used as a primary key
This is mainly used for indexing which we will learn later
Foreign key
A key which is used to link to a primary key of another table
This is how the relationship between tables are made
Referential integrity
The use of a foreign key ensures that a value can only be entered in one table if the same value already exists in the referenced table
This means that foreign key of a table can not be different from the primary key of the referenced table
This ensure that the values in the foreign key must match the primary key values
Firstly, the attributes are made, then the foreign and primary key are defined
Also the primary key can not be updated or changed/deleted if the foreign can't refer to the primary key
Entity relationship modelling
These are represented using E-R diagrams
An entity is an object,thing or person which can store data in fields and rows
So an entity has to have many instances or items to be displayed as a table
In relational databases the tables must be linked so the E-R modelling helps us to find the link between the entities
The exam will us scenario where a database is required to store data
1. First we need to identify the entities
2. Identify the type of relationship. Remember one to one relationships can be ignored
Cardinals or relationship
When finding the relationship between two entities we need to use logic
There are 4 types of relationships between entities and for each we will give an example
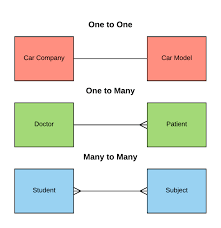
However we could also add some additional information
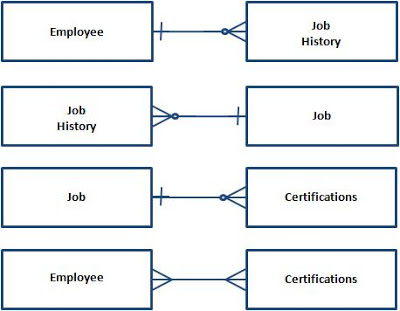
Detailed E-R diagrams are not usually tested so you can ignore them but you need to know how to draw a normal one
It means one instance is linked to one instance in the other table
An example is when one band contains many members
We usually say it like this
One is to many and many is to one
For example like a auction center where many people can bid for a single product(instance) and also many products could be auctioned by a single person
Forming the relationships are required and need practice
For example what is the relationship between a BAND and the MEMBER entities?
It is one to many
Representing this relationships in a diagram is called the E-R diagram and they usually give alot of hints
The E-R diagram doesn't just contain a relationship between just two entities but many entities
There are few things you need to remember everytime you see these questions
The table/entity which contains the foreign key is the Many side and the table/entity which contains the primary key is the one side. ALways remember this
No matter what keep this in your mind
Many to Many relationships
It is very hard to represent a many to many relationship in practical databases using foreign keys and primary keys - as then both tables must have foreign keys which is not right
So we make an intermediate table called a link entity which joins two entities which has many to many relationships
So the Link entity table is a separate table which has two foreign keys which are used to link the primary keys of each entities
The two foreign keys are both used as primary keys
We will see that more in normalisation
Normalisation
Normalisation is very similar to the E-R diagrams however, in normalisation this is organising already recorded data in the most efficient way possible whereas E-R diagrams are made before data is recorded
Usually groups of data in a flat line table or a stand alone table may have repeating groups and other inefficient things. Normalisation helps to break the single table to several tables called entities and links them together
There are 3 steps in normalisation:
1 NF or 1st Normalisation
The relations can't have repeating groups and so repeating groups are removed
Repeating groups are when the attributes have more than one set of the same values
Like the below example
| Surname | Department | Payrate | Country | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donaldson | Accounts | $25 | USA | New york |
| Newton | HR | $28 | UK | London |
| Xian | Accounts | $25 | China | Shanghai |
The attributes or fields which have the same value are grouped together in a non repeated table and it is linked to another table which contains an attribute which is repeating
So the relationship is one to many
Let's see the same example. This is in the 1NF
| Department | Payrate |
|---|---|
| Accounts | $25 |
| HR | $28 |
This table is then linked to a separate table.
| Department | Surname | Country | City |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts | Donaldson | USA | New york |
| HR | Newton | UK | London |
| Accounts | Xian | China | Shanghai |
As we can see the 2nd table has the repeating groups for the department field but not for the pay rate. So this ensures data redundancy is minimized as possible and it is very significant in large sets of data where many attributes have repeating groups
Also we can see the 1st table could be called the Jobdetails entity which the department field acts as the Primary key. The Employeedetails entity is referenced to the Jobdetails entity by using the foreign key department
So again by using the rule, the place which has the foreign key is the many sides and the one with the primary key is the one side
The relationship is one to many
Another point to remember is that the foreign key of the Employeedetails entity is department but what is the primary key. As the department field is not unique it is not enough to uniquely identify each record. So we need to define another key as a primary key.
The last name can be used as the primary key. However, we use both the departments and the last name as primary keys. This is because the foreign key of the new table must be also the primary key. So we will use the surname and departments as both primary keys
2 NF or 2nd Normalisation
A rule in the relational database model is that non-key attributes or the other attributes must depend fully on the primary key or keys. This means we must be able to identify each record uniquely depending on the primary keys only
However, sometimes the other attributes may not be dependant on both primary keys but only a single primary key. This is known as partial dependancy
I just realized the example above is very poor and just focus on the method. So I will state that the Country and city are dependants on the surname but not on the department key
The 2nd normal form removes any partial dependency and it must be already in the 1 NF to do this
| Department | Surname |
|---|---|
| Accounts | Donaldson |
| HR | Newton |
| Accounts | Xian |
| Surname | Country | City |
|---|---|---|
| Donaldson | USA | New york |
| Newton | UK | London |
| Xian | China | Shanghai |
As we see we made a separate table so that the country and the city are dependant on the primary key only. In the Surname origin table the primary key is the surname. Now in the previous table, the name changes from Employeedetails to Jobdetails - surnameorigin
This example is completely fictional and i just created it.
Now in the 2nd table(jobdetails-surnameorigin) both the Surname and Department keys are foreign keys as they link between the two tables
They are also both Primary keys
The relationship is many to one
This is the same as the link entity method to display a many to many relationship logically/practically
3 NF or 3rd Normalisation
Again back to the point that the non key attributes must depend only on the primary key.
Sometimes the non key attributes could be dependant on another non key attribute
For example the city depends on the country and so the 3rd normal form removes any Transitive dependancy(non - key dependancy). So a 4th table is made
| Surname | Country |
|---|---|
| Donaldson | USA |
| Newton | UK |
| Xian | China |
| Country | City |
|---|---|
| USA | New york |
| UK | London |
| China | Shanghai |
As we can see we made a separate table so the city field is only dependant on the country field
The primary key of this table is Country and the foreigh key is in the previous table
The relationship is many to one
Normalisation is a method and it is very tricky. But just remember these two principles
Normal forms can't have repeating groups or any partial or transitive dependancy
Database Management System (DBMS)
The database management system can be divided to 3 levels
This is the level used by the external users of the data in the database. Where they store and retrieve data without any knowledge of the structure of the database. They have access rights to control which data they are able to access
The employees in a company use this level
This is the level used by the DBA (Database adminstrator) who creates tables and databases. The DBA is also responsible in setting access rights for the users in the external level. The DBA uses the DBMS software to perform these functions
This is the level handled by the DBMS software which controls the storage of data in the physical storage(internal schemes). It controls where data is stored in the storages and this is the level where data is directly accessed or stored
DBA
This is the person who is in charge of the conceptual level and uses the DBMS software to create the structure of the database
There are some tasks which the DBA is in charge of and you need to know these
1. Setting up Regular and incremental Back ups
2. Setting up the access rights for users in the external level
3. Creating databases and tables and their relationships
4. Data dictionary and indexing function could be used by the DBA
DBMS Software
This software controls the whole database and allows the DBA to create tables and the external usere to store or retrieve data
In other words the DBMS software handles the internal operations of the database
Usually the DBA doesn't require to know SQL to be able to create the databases or to access or store data
The Developer interface provides an interface for the DBA to create the structures easily
The Query processor is a special software which is used to retrieve/ manipulate data in the database
You will need to know the features provided by the DBMS software
1. Performs daily and incremental backups
2. Sets access rights for each user
3. Validates data when entered - maintains data integrity
4. Indexing function to access data faster
5. Data dictionary - which gives the detal of how the data in the database are stored in the physical memory to the DBA
Indexing
A small secondary table which contains an attribute of unique values so it can point to the tuple of the table much faster
This concept makes accessing data from a large table much faster
A separate table called an index table contains an attribute of the table which contains unique values(candidate key)
We usually use the secondary key for this , so the index table points it to the corresponding tuple for fast access
SQL
We need to learn some scripting of the SQL language
SQL is divided into two categories
To define the structure of the database
In manipulating the data in the database such as storing and retrieving data from the database
In reality we don't really separate the language to these two parts
We will show an example for each
DDL
We will see an example
Creating Database structures:
CREATE DATABASE ClientDatabase; CREATE TABLE Clientdetails(PRIMARY KEY(Client ID varchar(10)) ,ClientName varchar(25),DOB Date,Subscription boolean); ALTER TABLE Client-booking ADD PRIMARY KEY(Booking ID varchar(25)) ADD FOREIGN KEY(ClientID REFERENCES Clientdetails(Client ID);
As you can see we need to remember some points
SQL is Case Insensitive
The program statements can go for many lines but each statement must end with ;
We use the Keywords DATABASE and TABLE only in DDL and not in DML
So when we want to define an attribute as a primary key we need to put it in brackets
The ALTER keyword is used to alter an existing table such as adding a new field
For each attribute we need to define the data type, databases don't contain the datatype STRING so we use varchar(x) where x is number of characters
The Database follows all other datatypes except STRING
DML
- Adding data to the table
INSERT INTO Clientdetails(Client ID, DOB) VALUES (2345, 23/7/2002);
There is another way of entering but this is the correct one
The clientdetails is the table name and inside the brackets are the field names
The values must be in the same order as the fields in the brackets
SELECT DOB FROM Clientdetails WHERE Client ID = 2345;
So this will return 23/7/2002
We need to select which field name you need to be displayed and from which table and also the where statement gives us the condition or else the whole DOB attribute will be displayed
SELECT DOB FROM Clientdetails;
We can also display all the fields using the *
SELECT * FROM Clientdetails WHERE ClientID = 2345;
So this displays all the fields in the table clientdetails
If we need to have some format of displaying the data we can either use:
SELECT DOB FROM Clientdetails WHERE ClientID = 2345 ORDER BY DOB ASC|DSC;
or we could use:
SELECT DOB FROM Clientdetails WHERE ClientID = 2345 GROUP BY Department;
This means that the date of birth is displayed in groups of department
If the department has repeating groups then this could be used
The WHERE condition could be further used to compare field values of different tables and not only in the same table
SELECT DOB FROM Clientdetails INNER JOIN Client-booking WHERE Clientdetails.ClientID = 2345 AND Client-booking.BookingID = 2345;
So this is used to display the field value when both conditions of two different table values are correct
We need to use INNER JOIN to join the other table. We also need to use a dot to show it is a field of a particular table
Clientdetails.ClientID means the field ClientID from the table Clientdetails
If we need to change the existing data in the table
UPDATE CLientdetails SET ClientID = 2678 WHERE ClientID = 2345;
So this changes the clientID which was 2345 to 2678
DELETE FROM Clientdetails WHERE ClientID = 2678;
If the client is no longer in the business then we need to delete it them from our table
This deletes the whole record which has the the ClientID 2678
Always remember the foreign key records must be first deleted before the primary key records are deleted in the referenced table (referential integrity)
Summary
I will give a small summary of each keywords
CREATE - DDL for creating databases or tables
DATABASE or TABLE - DDL used for defining the name
ALTER - DDL change the structure of an existing table such as adding a new field/attribute
ADD - DDL used in adding new fields
INSERT - DML inserting new data to a table
VALUES - DML order of the values to be inserted in to the corresponding fields
SELECT - DML retrieving data
FROM - DML Identifys from which table
WHERE - DML conditions
GROUP BY - DML groups displayed data
ORDER BY - DML orders displayed data
INNER JOIN - DML used to compare field values from two different tables
UPDATE - DML used to update a table
SET - DML sets a field to a value
DELETE - DML deletes a record from a table
Recommended
These are things you might like. Clicking these ads can help us improve our free services in the future...
End of Chapter Videos
Collection of Videos to Support Your Understanding.
Remember these videos are handpicked by me and I feel these are one of the best ones out there. But I constantly update this list for each chapter.The Youtubers are more than welcome to contact me.
Also, don't forget to Subscribe to our Youtube channel - Wiscus
Watch
