Physics AS
Introduction Physical Quantities & Base units Vectors & Scalars Kinematics Pressure & Density Dynamics Momentum Energy, power & efficiency Deformation of solids Waves Superposition Stationary waves Electric fields Electricity Circuits & Kirchoff's laws Radioactive Physics AS PracticalPaper 5More
Reference Pastpaper QuestionsSuperposition, Interference & Diffraction Grating
Superposition
When two or more waves meet, a resultant wave is formed in which the displacement is the sum of the individual displacements of the waves
You need to know somethings in superposition. It is a highly general term and so there is no thing called constructive and destructive superposition
The idea is very simple, when two waves meet they form a resultant wave, the waves do not need to be coherent and identical in frequency. The resultant wave formed can be larger than the individual waves or smaller. Either one has no specific term.
You will need to know how to draw the resultant wave
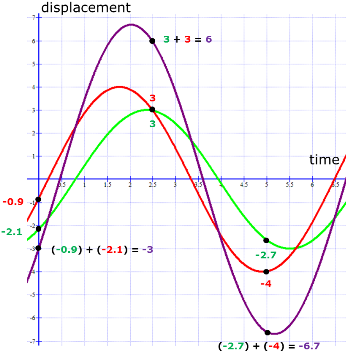
When they give two waves, they each have a displacement at a particular point - either positive or negative or same.
At different points, take the sum of the displacements of the two wave at that particular time like above and so plot the resultant wave points
When you have enough points, draw the smooth wave curve
Interference
Interference is a highly specific category under superposition which deals with only coherent waves and has specific terms when the maximum resultant and the minimum resultant is formed.
It is when two coherent waves meet, the resultant wave displacement is the sum of the individual wave displacements
Coherent waves
When two or more waves have a constant phase difference at any given time
So as we know what are coherent waves, we will talk about the specific terms of interference, but before that we need to know what's out of phase and in phase
Out of phase/Antiphase - Destructive interference
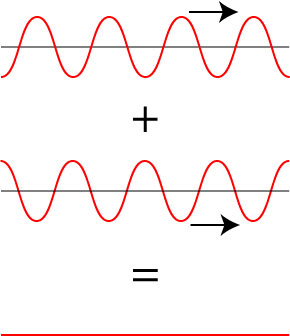
It is when coherent waves with a phase difference of 180 or π meet to interfere destructively
It always is 180° and so it is a specific term or difference. At this point, the waves fully cancel out each other in the maximum way as possible, resulting in the lowest resultant wave displacement
Inphase - Contructive interference
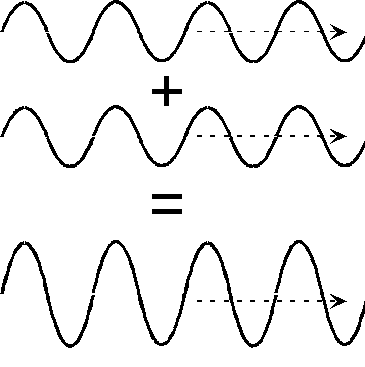
It is when coherent waves of phase difference of 360° or 2π meet to interfere constructively
It always is 360° and so it is a specific point or difference. At this point, the waves fully joins together in the maximum way possible, resulting in the Highest resultant wave displacement
What about other phase difference angles?
It is not truly destructive or constructive. However, we just need to know the two specific angles in which the maximum and the lowest resultant is formed
Notes to remember
As mentioned, phase difference increases every 360°, which means the destructive interference at 180° is also the same as 540°. The phase difference of 360° is same as 0° and also the same as 720° and so on
Also waves do not have to be the same amplitude but, must have the same frequency (coherent).
Lastly, this point is quite important:
Interfernce pattern
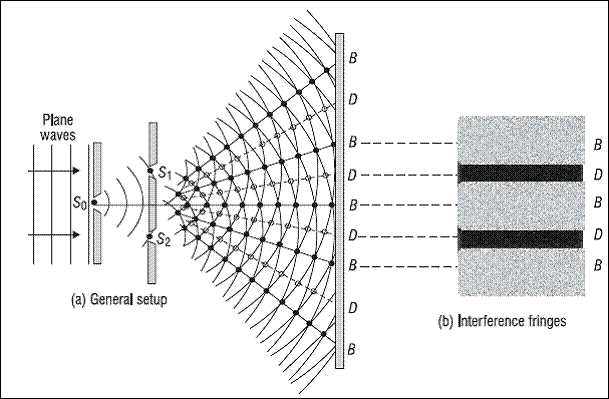
It is when two coherent waves meet to form an interference pattern both destructive and constructive interference onto a screen
Remember interference pattern must have both maxima and minimas
So an interference pattern must have both to identify it is a pattern
How are two coherent waves formed?
Usually when doing experiments we need to have two or more source which produce coherent waves so they can interfere
This is done by using a single wave source behind a barrier which has two or more gaps and when the waves pass through the gaps they diffract and curve but, they still have the same frequency or wavelengths. So then they can interfere to produce an interference pattern
Diffraction
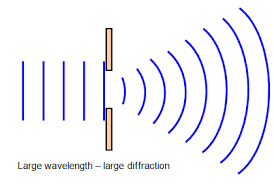
It is the spreading of waves as they pass through a gap/slit
So they have curved waves which has the same wavelengths as before
There is an important point you need to remember:
- The diffraction is greater when the wavelength is equal to the gap width
- Diffraction is required for the waves to meet. Points where the crest and crest meets, they are in phase and so interfere contructively. Points where the crest and trough meets, they are out of phase and so interfere destructively
- Each maxima is called the nth order maxima
- The next point a maxima is formed it's called the first order maxima.
- The set up is symmetrical
- The angles between orders are not same
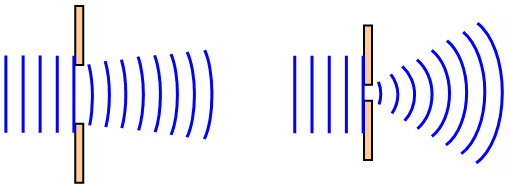
However in MCQs, it is more trickier as they state that the diffraction angle ( amount of diffraction ) increases when the gap width decrease until it is optimum when the gap is equal to the wavelength
But if the gap width is greater than the wavelength, the amount of diffraction is less, so if you decrease the wavelength and keep the gap width constant, the diffraction angle decreases
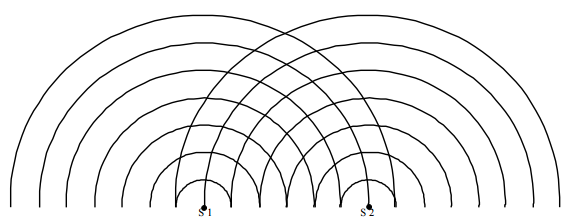
The point where they interfere contructively, they produce a maxima or a bright fringe. Points where they interfere destructively, they produce a minima or a dark or weak fringe
But how to calculate if the waves are interfering constuctively or destructively, We need the idea of path difference!
Diffraction angle and more
So what is the diffraction angle, We know as waves spread the direction of the wave energy spreads, and so the angle between these direction of the wave energy is called diffraction angle.
Greater the diffraction, greater the angle
What if the gap is very small?
This principle is used in microwaves. So as microwaves have a wavlength in cm, the gaps in the grills of the microwave are quite small. This do diffract the waves but the wave power doesn't pass that much. In order words, the wave is reflected back
Path difference
It is the difference of distance moved by two waves from its sources to the point where these two waves meet
So why do we find the difference in length. This actually shows whether a wave is ahead of each other or not. Also to see if they meet at a crest or a through
So we get the path difference in meters
After that, if the path difference is not zero, it shows that one wave is ahead of the other. But by how much? Half a wave, a wave or 2 waves...
Path difference = l1 - l0
Path difference = n(wavelength)
Path difference = nλ
We know wavelength is the distance of one complete wave so when the path difference is divided by wavelength, it shows how many wavelengths or waves ( in terms of a number ) the waves are apart
After finding n ( which has a special meaning - orders or the points called maxima ). If n is whole number, it means that some number of waves is a wholenumber of waves ahead. This shows that the phase difference is zero.
n = If integer, phase difference is 360 or 0 degrees
If n Ends with .5 for example 0.5 and 1.5 and 2.5, this means that the waves have a phase difference of 180° and so they are out of phase and so they interfere destructively
Young double split experiment
This experiment is useful in finding the wavelength of a wave source
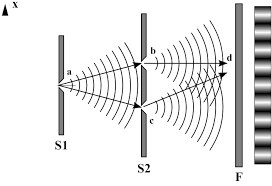
Wavelength = ( Split seperation * fringe seperation )/ Distance from screen
λ = ax/d
a - is the seperation of the slits
x- is the seperations between two nearest bright fringes or dark fringes
There is an important part:
The distance between two nearest fringes(dark or bright) are always x and remains the same.
Distances between a dark fringe(minima) and the bright fringe(maxima) is half of x and it also remains constant anywhere
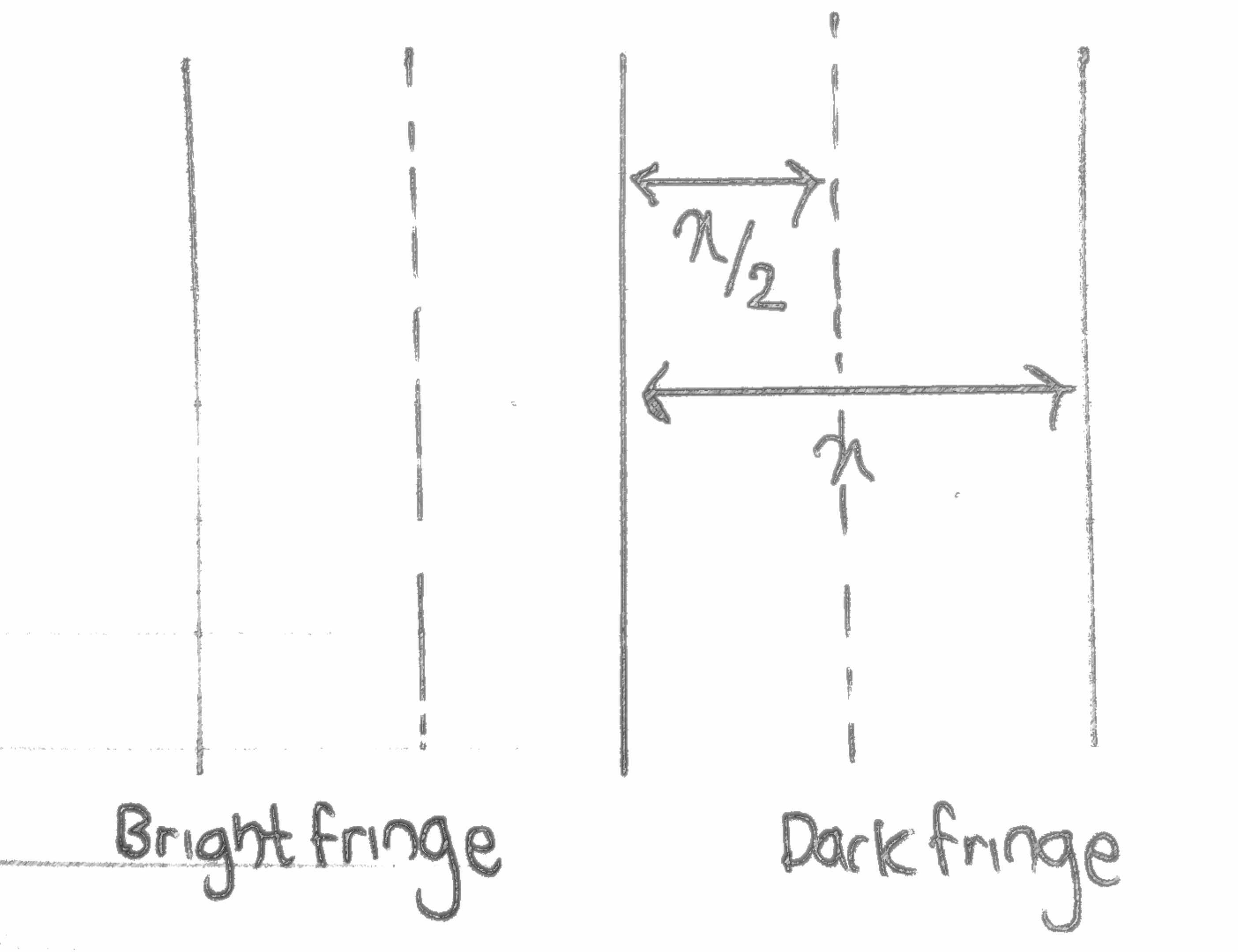
So to find x we may need to multiply the distance between a maxima and minima by 2
It doesn't really matter which is a or x. Just keep each consistent
So this is used in experiments to find the wavelength of a light source. The two light sources must be coherent.
Diffraction grating
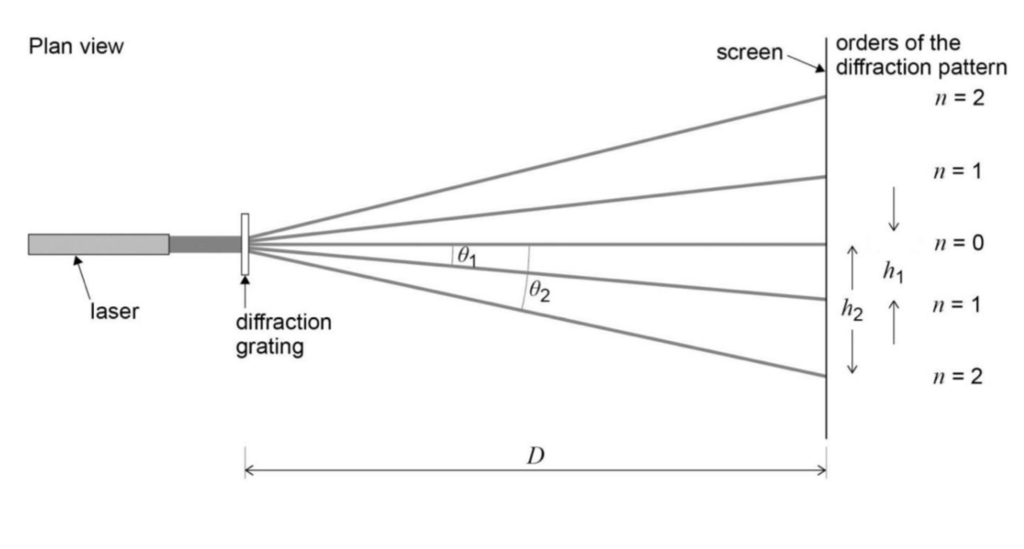
When we we have more than two slit, we get a inteference pattern. However, the maximas are more spaced out and more sharp!
dsinθ = nλ
So d is actually the slit seperation and because it very small, it is found by a method
The angle θ is the angle from the order to the central maxima
The n has a special meaning in diffraction grating:
The central maxima is called Zeroth order maxima or 0th order maxima
So the nth number increases each time there is a maxima
So the equation above gives the angle of the order from the Zeroth order maxima
Diffraction grating notes
There are some important points you need to remember
So angles to the zeroth order on one side is same as the angles on the other side. So it is symmetrical in the zeroth order plane
So the angle between the two 2nd orders is the twice as the angle from the 2nd order to the zeroth order
This is an important point! In fact the distance between the maximas are not the same and also the angles between them are not the same.
If you need to find the angle between two maximas. First, find the larger angle to the zeroth order and minus the smaller angle to the zeroth order

dsinθ = nλ
θ = sin-1(nλ/d)
So find the angle when n is 2
θ1 = sin-1(2λ/d)
So find the angle when n is 1
θ2 = sin-1(1λ/d)
θ2-1= θ1-θ2
So this is the angle between the first order and the second order
Calculating d
This is actually known as the slit seperation or grating spacing or slit spacing
There is a common misconception that d is the slit width, but this is wrong. It is actually the seperations between the slits. So its similar to the young double slit experiment. However, as the slit seperation is very small, we use the term slit spacing instead.
They usually give the number of line/slits per mm or meter
So for example, if they say 600 lines per mm
d = (1mm/1000)/600
We divide by 1000 to convert it to meters
Diffaction grating for white light
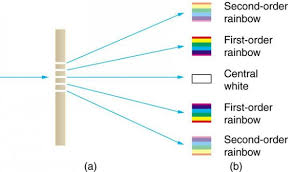
We have only looked at single wavelength questions but, white light contains a variety of wavelengths. When the white light passes through the slits, the light splits into many colors. This is called dispersion.
So each wavelength of light would have its own maxima on the screen
The variety of colors can only be seen in a diffraction grating and not in a young double slit because the maximas are more far apart
Now you need to remember that the central maxima is always a white maxima. This because for any wavelength of light it always meets at the center, so this would anyways produce a white light.
So shorter wavelengths such as violet will have a smaller angle according to this equation
dsinθ = nλ
sinθ ∝ λ
So when the wavelength is greater(red) the angle is greater
So it will be white in the center then violet closest to the center and then red furthest away
Recommended
These are things you might like. Clicking these ads can help us improve our free services in the future...
End of Chapter Questions
Collection of Topic Questions to understand the topic more.
You need to do the next chapter also to be able to answer pastpaper questions - Stationary waves
End of Chapter Videos
Collection of Videos to Support Your Understanding.
Remember these videos are handpicked by me and I feel these are the best ones out there. But I constantly update this list for each chapter. The Youtubers are more than welcome to contact me.
Also, don't forget to Subscribe to our Youtube channel - MrWik
Watch
