Chemistry
Introduction Moles Empirical Formulas & More Atomic Properties Ionisation Energies Bonding Intermolecular Forces States of Matter & Ideal Gases Giant Covalent & Ionic Structures Enthalpy Change Hess's Law Reaction Rate Equilibrium Redox Reactions Periodicity Group 2 Elements Group 7 Elements Nitrogen & SulfurOrganic Chemistry
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Organic Reactions Alkanes Alkenes Halogenoalkanes Alcohols & Carboxylic acids Aldehydes & Ketones PolymerisationMore
Reference Chapter QuestionsGroup 7 Elements
Basics
Group 7 elements are also called Group 17 elements or Halogens
They are present as Diatomic atoms always
They end with an electronic configuration of P5
They only have weak induced dipole forces between molecules as they are non polar
Melting & Boiling points
There is a clear increase in boiling and melting points down the group. This is because due to the increase in induced dipole forces between molecules. The increase in electrons increases the induced dipole forces!
Properties
The properties of the main halogens are given. You need to remember these points
| Halogens | Formula | Color | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorine | F2 | Pale yellow | Gas |
| Chlroine | Cl2 | Pale green | Gas |
| Bromine | Br2 | Brown orange | Liquid |
| Iodine | I2 | Black / Gray | Solid |
Oxidising Power
Halogens are powerful oxidising agents but, their oxidising power decreases down the group. This means that down the group, they get easily oxidised
For example:
2NaBr + Cl2 → 2NaCl + Br2
This shows that chlorine is a more powerful oxidising agent than bromine. In fact, this is a displacement reaction and this is used to show that the reactivity decreases down the group
Solubility of Halogens
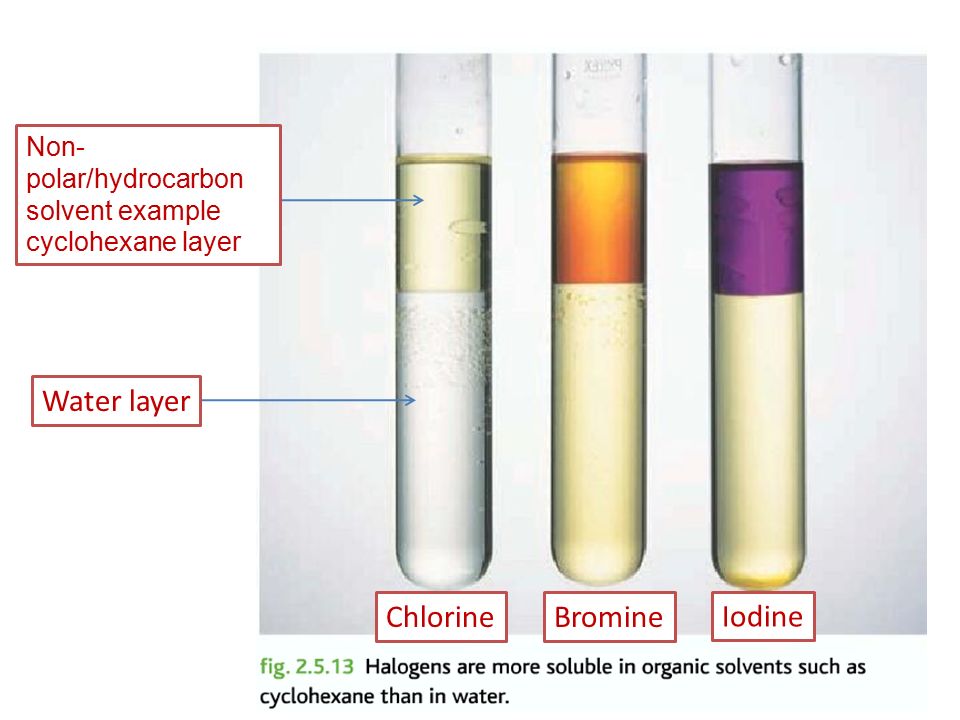
Halogens are slightly soluble in water and they are present in the diatomic state. However, halogens are very soluble in cyclohexanes. In fact, when dissolved they have their unique colors
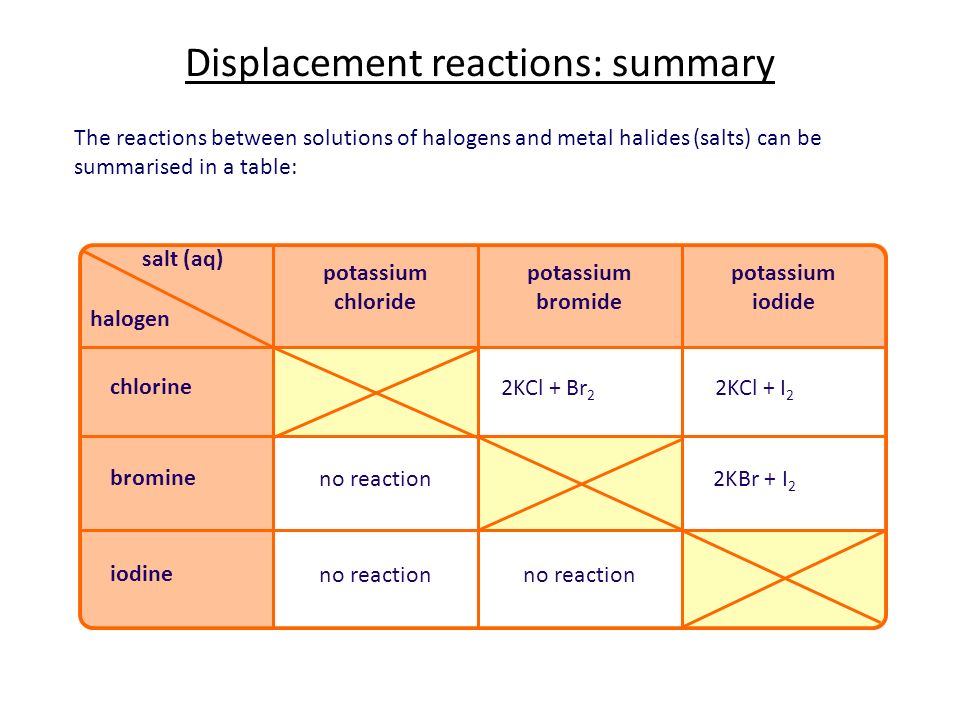
Displacement Reactions
When the more reactivity element displaces the less reactive element from its salt solution
Like the above example, Chlorine gas will displace bromine from its salt solution
This table will summarise whether a reaction will occur. Always remember the more reactive one will displace the less reactive element or else there will be no reaction
Hydrogen Halides
When a halogen reacts with hydrogen, a hydrogen halide is formed. For example:
Br2 + H2 → 2HBr
We will consider how each halide reacts:
| Name | Process | Stablity |
|---|---|---|
| HF | Reacts explosively under cool and dark conditions | Most Stable |
| HCl | Reacts explosively in sunlight | |
| HBr | Reacts slowly to form a stable product | |
| HI | Reacts very slowly to form an unstable product that decomposes. Forms an equilibrium | Least Stable |
The stability decreases down the group. This means that the HF molecule is more stable than HI
This is because, the bond enthalpy or strength of HF is more stronger than HI. As HI has the weakest bonds, it is very unstable and easily decomposes
Reactions with Conc Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a powerful oxidising agent also and it is powerful enough to oxide bromine and iodide ions but, not Chlorine. Instead, it acts as an acid
When Concentrated sulfuric acids is added to Sodium Chloride crystals, HCl gas is made.
2NaCl + H2SO4 → 2HCl + Na2SO4
This is not a redox reaction but an acid base reaction as sulfuric acid only acts as an acid. This is important for the production of hydrogen chloride gas.
The products are further oxidised. The first equation is the same which means in this reaction sulfuric acid acts as both an acid and an oxidising agent
2NaBr + H2SO4 → 2HBr + Na2SO4
NaBr + H2SO4 → Br2 + SO2 + H2O
This will give a mixture of products so it is a bad way to make HBr
The above 2 equation are the same but the products oxidise further
2NaI + H2SO4 → 2HI + Na2SO4
NaI + H2SO4 → I2 + SO2 + H2O
NaI + H2SO4 → I2 + S + H2O
NaI + H2SO4 → I2 + S + H2S
The understanding is very simple but, it is good to remember these equations and the products
This reaction will release white fumes ( HI ), a yellow solid (S) & rotten eggs smell and Purple fumes
In fact all of these above reactions will release white fumes as a hydrogen halide gas is formed
Test For Halides
We add aqueous silver nitrate and nitric acid to test the ion. Then we add aqueous ammonia to distinguish them
| Halide | Silver Nitrate | Then add Ammonia |
|---|---|---|
| Chloride | White ppt | Dissolves in Dilute Ammonia |
| Bromide | Cream ppt | Dissolves in excess concentrated ammonia |
| Iodide | Yellow ppt | No visible change |
The reason why the precipitate dissolves in ammonia is because a complex ligand structure is made. More will be covered later
Another important point to remember is that iodide compounds undergo a faster chemical reaction than chloride compounds. This is also again due to the weak bonds in the iodide compound. So it has a lower activation energy and so it reacts faster. This means for the above table, the yellow ppt is formed first then cream then white
Fastest Iodocompounds . . . Slowest Flurocompounds
Disproportionation
A process in which the atoms of an element both oxidises and reduces simultaneously
This means that the products are an oxidised and reduced form of the reactant. We use NaCl + Cl2 as the example. At different conditions, different products are made
NaOH + Cl2 → NaCl + NaClO + H2O
As you can see one chlorine has an oxidation number of -1 and the other one has an oxidation number +1 in NaClO. NaClO is used to make bleach to kill bacteria
NaOH + Cl2 → NaCl + NaClO3 + H2O
Now we see that one chlorine atom has an oxidation number of -1 and the other one is +5
These equation must be memorised and the products and oxidation numbers must be known as they exams do ask you
Uses of Group 7 Elements
There are many uses of group 7 elements but we will only note down the important ones:
Chlorine is added to water to bleach and sterlize the water by killing harmful bacteria
H2O + Cl2 → HClO
HClO → HCL + [O]
This decomposes to HCL and activated oxygen that kills bacteria
They are simply used in many situations such as disinfectors, retarder, textile and to make hydrogen halides and gases such as HFC or CFC that are inert and used in aerosol sprays and refrigants
They are used to make polymers such as PVC or Teflon ( polytetrafluroethene ) that are strong. More will be dicussed in the polymerisation section
