Chemistry
Introduction Moles Empirical Formulas & More Atomic Properties Ionisation Energies Bonding Intermolecular Forces States of Matter & Ideal Gases Giant Covalent & Ionic Structures Enthalpy Change Hess's Law Reaction Rate Equilibrium Redox Reactions Periodicity Group 2 Elements Group 7 Elements Nitrogen & SulfurOrganic Chemistry
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Organic Reactions Alkanes Alkenes Halogenoalkanes Alcohols & Carboxylic acids Aldehydes & Ketones PolymerisationMore
Reference Chapter QuestionsPolymerisation
The process of bonding small units called monomers to build a large chain known as the polymer
Polymerisation occurs under high temperature and pressure and for some reactions we use a catalyst
We will be only discussing a bit of addition polymerisation because this chapter will be fully covered in A2 Chemistry
Addition polymerisation
Addition polymerisation is an addition reaction which means only a single product is made
n(CH2=CH2) → -[CH2-CH2]-
We use some special terms such as monomers and polymers for reactants and products. The monomer must have a carbon double bond so it must be an alkene. The reaction occurs when the π bond breaks to form longer chains of carbon atoms
We will see the formation of some common polymers and their uses:
This uses the monomer ethene to form the large polymer polyethene
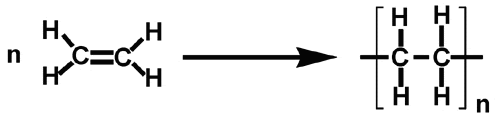
Polyethene is used to make plastic bottles and bowls as it is hard but flexible and a good insulator
This is similar to polyethene but we use the propene molecule to form polypropene
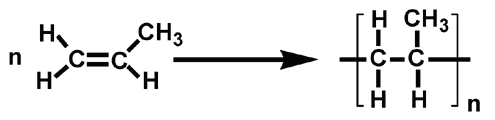
It is very strong so it is used to make plastic ropes and plastic crates
This uses the Chloroethene monomer to make the polymer Polyvinylchloride or Polychloroethene
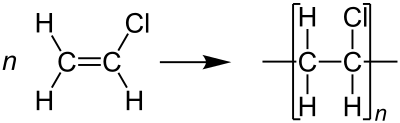
This is used as a insulator and to make taps and pipes because it is very hard but not very flexible.
This uses the styrene monomer to make the polystyrene polymer
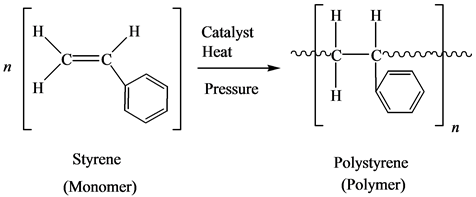
This is mainly used for packaging purposes as styrofoam. It is a good insulator!
The Tetrafluoroethene monomer is used to form the Polytetrafluoroethene polymer. This polymer is also called Teflon
Teflon has a high melting point and a non stick surface so they are used in cooking pans and also for taps and joints
Identifying the Monomer
In order to identify the monomer used in a polymer chain by just looking at the polymer chain. First we need to identify the repeating unit.
These are some repeating units:
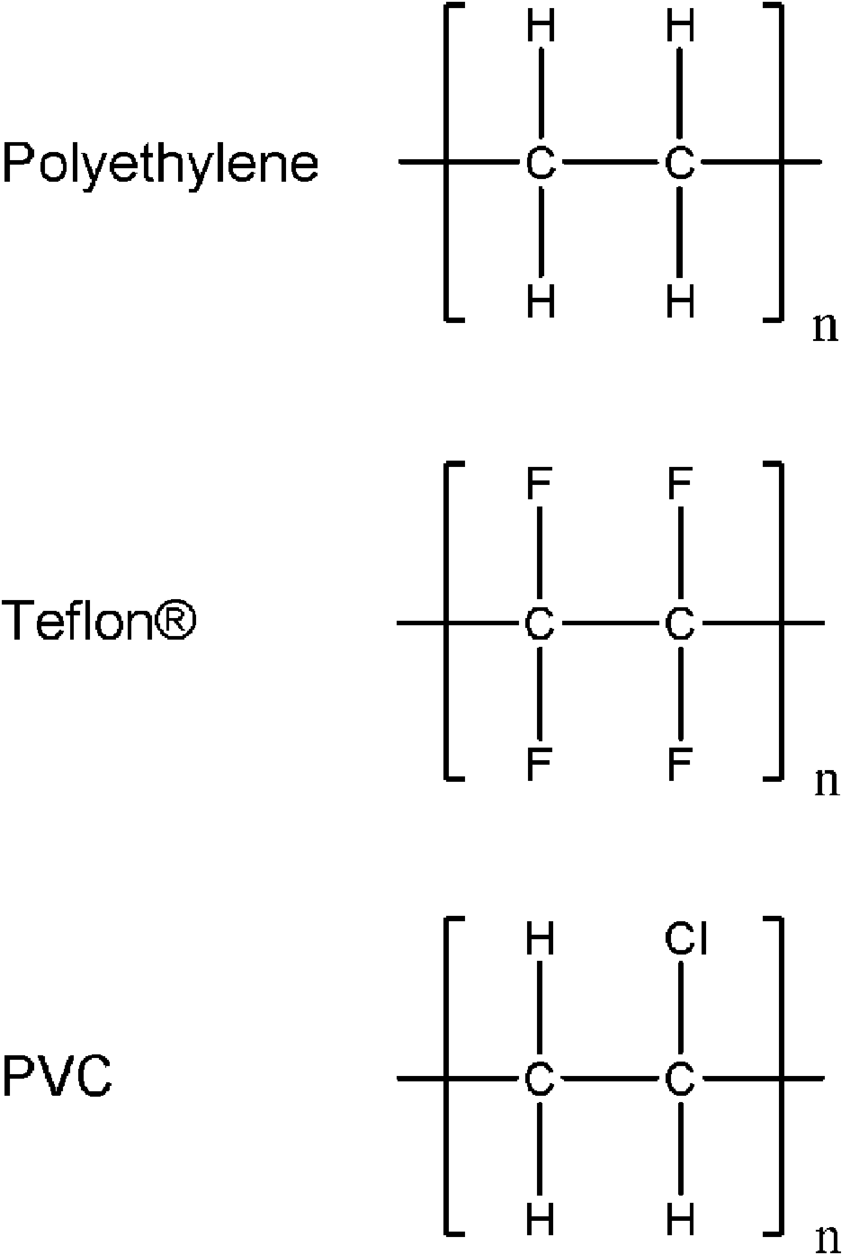
A repeating unit is a group of atoms which seems to be repeating across the carbon chain. This represents the monomer that was used to make the polymer
All you have to do is add a double bond to the repeating unit to get the monomer
Another point to remember is that the monomer can have Cis or Trans Isomers but when polymerised, it will not matter as there is only one bond!
Disposing Polymers
All of the above addition polymers are non-biodegradeable so they can not be broken down by the enviroment. The main problem arises when disposing these polymers. We will see some problems:
1. When burnt, can release energy but, also harmful gases such as HCl
2. Takes space and causes visual pollution
3. Can cause drains to flood and can release toxics
4. Kills marine life as they mistake it for food
