Chemistry
Introduction Moles Empirical Formulas & More Atomic Properties Ionisation Energies Bonding Intermolecular Forces States of Matter & Ideal Gases Giant Covalent & Ionic Structures Enthalpy Change Hess's Law Reaction Rate Equilibrium Redox Reactions Periodicity Group 2 Elements Group 7 Elements Nitrogen & SulfurOrganic Chemistry
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Organic Reactions Alkanes Alkenes Halogenoalkanes Alcohols & Carboxylic acids Aldehydes & Ketones PolymerisationMore
Reference Chapter QuestionsTypes of Organic Reactions
We need to know the type of reactions that organic compounds undergo
| Reaction | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Addition | This will only create a single product. This is usually the reactions of Alkenes |
| Substitution | An atom in the compound is replaced by another atom or group of atoms. Results in many products |
| Elimation | A General reaction in which it removes a small molecule from the substance |
| Dehydration | Removal of a water molecule from the compound. This can also be an elimination reaction |
| Condensation | Creates a product AND also another small molecule such as HCL or Water |
| Hydrolysis | Breaking down the substance using a water molecule. Usually forms two products |
Let us discuss these reactions more in depth and let us also see an example for each
Addition reaction
In this reaction all of the reactant atoms are in a single product
C2H4 + H2 → C2H6
Also addition polymerisation is a type of addition reaction. We do not need to know much about polymerisation in AS but we do have a separate chapter to discuss it!
Substitution
A good example is when a halogenoalkane is converted to an alcohol. This is done by replacing the halogen atom with an OH group
C2H5Br + H2O → C2H5OH
Elimination
This is a broad category and dehydration goes under this category
C2H5Cl + H2 → C2H4 + HCl
When any molecule except a water molecule are removed from the substance, we can say it is an elimination reaction
Dehydration
So when atoms of a water molecule is removed from the substance
C2H5OH → C2H4 + H2O
Condensation
This will release H2O or HCl as a Bi-product
C2H5OH + CH3COOH → C2H5O2CCH3 + H2O
This is not dehydration as even though a water molecule is released a new larger product is also formed
Hydrolysis
The addition of water breaks down the molecule. This is the opposite of a condensation reaction
C2H5O2CCH3 + H2O → C2H5OH + CH3COOH
This is an example of hydrolysis of esters and it is used to make alcohols and carboxylic acids from esters
Usually this is done by using an acidic/basic medium
Markovnikov's rule
This rule is used to predict the stability of the carbocations formed. There are 3 types of carbocations:
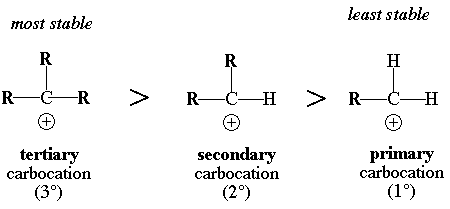
The Primary Carbocation has a single R groups and 2 hydrogen atoms. This is considered to be the least stable
The Secondary Carbocation has two R groups and 1 hydrogen atom
The Tertiary Carbocations has 3 R groups attached. This is considered to be the most stable
An R group can be either an alky group or a long chain of carbon atoms
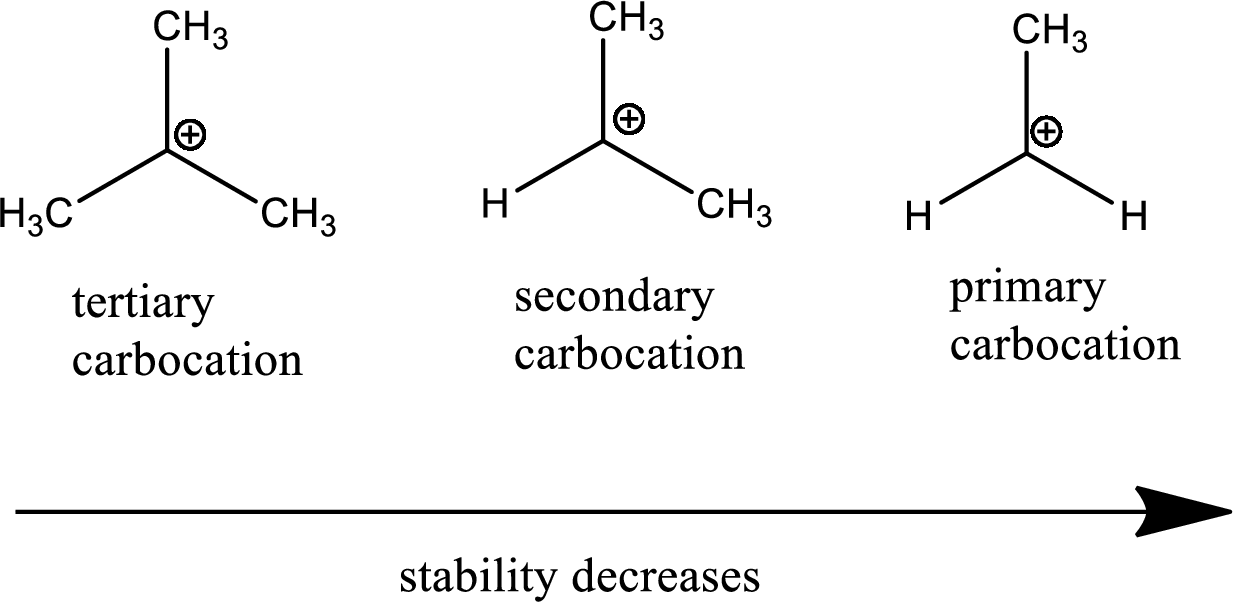
The reason why when there is more R groups, the carbocation is more stable is because, the R group are electron donators which means they push electrons from them. This is known as the positive inductive effect and so when more electrons are pushed towards the carbocation it is more stable. This is why when there are more R groups, it is more stable
This can be used to determine the abundance of specific compounds. The carbocation which is the most stable will give the higher concentration of products
Homolytic vs Heterolytic Fission
Usually when a reaction occurs, bonds must be broken. There are two ways in which bonds can be broken and they are:
Breaking of a bond that result each atom to recieve an electron from the bond. This will result in the production of free radicals and this is not a redox reaction!
Breaking of a bond in which one species or atoms recieve both electrons. This will result in a postive and negative ion and this is a redox reaction
